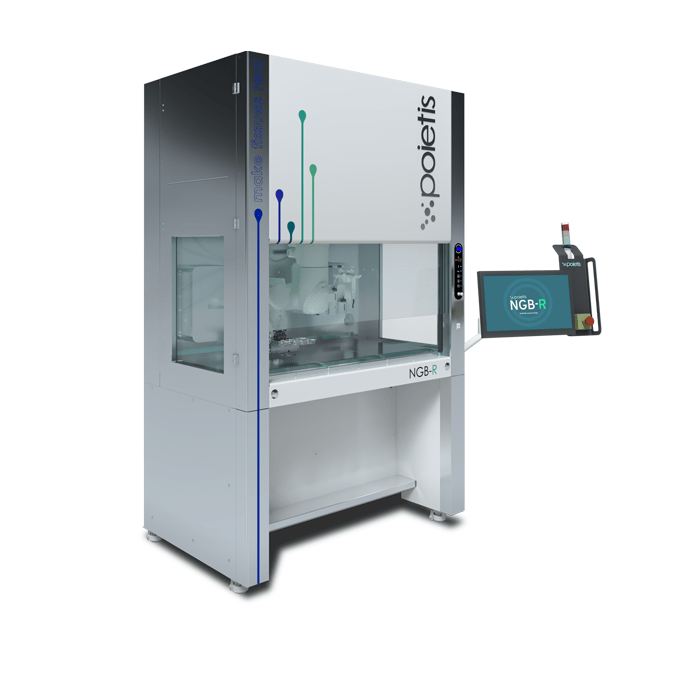
Poietis NGB-R
Scalable automated 4D bioprinting

Next Generation Bioprinting (NGB) plaform has been developed to overcome current tissue manufacturing methods which are the bottleneck impeding standardisation, scale-up and large-scale market adoption of Tissue-Engineering products.
-

Key Features
- Computer-Assisted Design. NGB platform integrates a specific « cytocentric », user-friendly CAD software.
- Automated, robotic bioprinting with easy-to-use bioprinter based on laser-assisted bioprinting.
- Multimodal traditional extrusion and micro-valve print-head options for complete flexibility in tissue type and complexity.
- In-line monitoring of the print process combined with IA machine learning algorithms
- Tissue formation modeling via dedicated software to program tissue self-organization
Next Generation Bioprinting (NGB) platform has been developed to overcome current tissue manufacturing methods which are the bottleneck impeding standardisation, scale-up and large-scale market adoption of Tissue-Engineering products. It solves critical limitations of existing 3D bioprinting technologies thanks to single-cell resolution and learning-based methods.
Indeed, largely inspired by the principles of the 4.0 Industry, this new platform integrates automation and robotics technologies, coupled with numerous online sensors – including cell microscopy – and Artificial Intelligence processing. In addition, it integrates all bioprinting techniques (laser-assisted bioprinting, bioextrusion, micro-valve bioprinting), a world’s first in the bioprinting market.
-
Designing 3D Biological Structures with CAD
NGB platform integrates a specific « cytocentric », user-friendly CAD software. This software can be used to design the location and local environment of different cell types and materials in three-dimensional tissue structures.
CAD files describe the architecture of biological tissues with the 3D organisation of tissue components (cells and extracellular matrix).
-
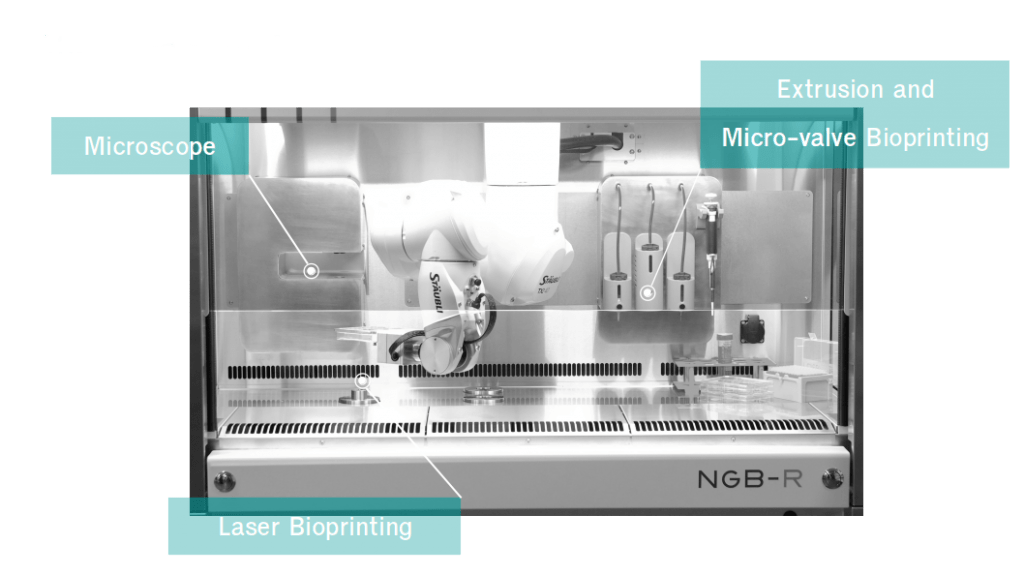
Integrated Multi-Modal Bioprinting
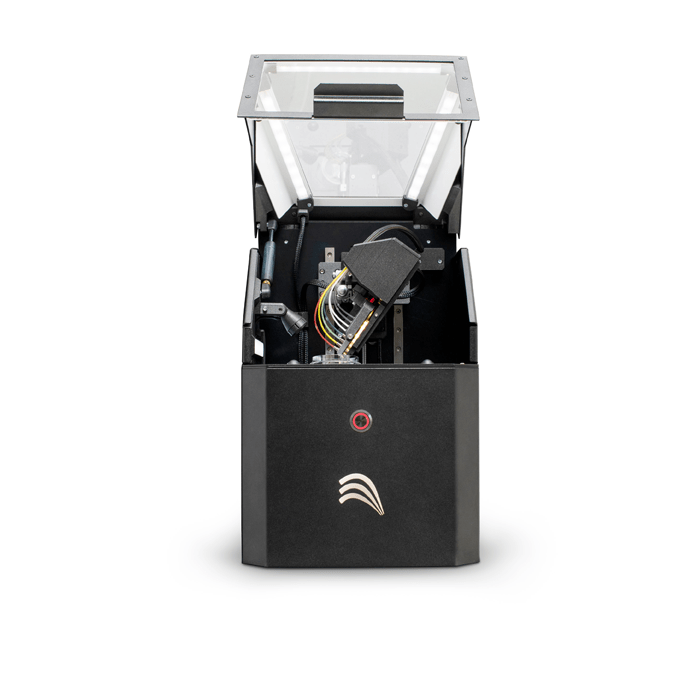
NGB platform integrates a multimodal, easy-to-use bioprinter based on laser-assisted bioprinting capable of 3D-printing tissue components in sterile conditions, with great accuracy and reliability thanks to 6-axis robotic arm and automation. This bioprinter is now the 4th printer version from the beginning of the project in 2005 and the only fully mutlimodal on the market.
-
Laser-Assisted Bioprinting in Action
Laser-assisted bioprinting makes it possible to print cell by cell according to the following physical mechanism. The focusing of a laser pulse (in blue) on a cartridge (composed of an ink film spread on a glass plate) results in the formation of an ink jet towards a substrate on which cell microdroplets are collected. By controlling the physical conditions of the ejection (energy, viscosity…), the volume of the droplets is controlled precisely (~ picoliter).
The cell patterns are obtained by rapid scanning of the cartridge by the laser, which results in the formation of 10,000 droplets per second.
-
Accurately Bioprinting Designs
Bioprinting technologies have been combined with a specific imaging system coupled with AI machine learning algorithms to confirm that what is designed is what is bioprinted.
-
The Evolution of Bioprinted Constructs
Data generated at all steps of the process are used to model tissue formation. A dedicated software is now under development to program tissue self-organization, which means to anticipate the evolution of the bioprinted construct with time.
-
Making the Most Out of the NGB-R Bioprinter
All you need to know about the Poietis next generation NGB-R bioprinter:
- 0.22min – 1. Poietis introduction
- 2.35min – 2. NGB-R in a nutshell
- 7.40min – 3. A Cytocentric Approach to Bioprinting
- 9.05min – 3.1. Printing cells separately & no need for commercial bioinks
- 16.22min – 3.2. Defining 4D bioprinting & cell patterning
- 21.00min – 3.3. On-board imaging to take bioprinting farther
Run time: 26.38min

- All
- Additive Manufacturing
- Biological Microscopy
- Bioprinting
- Cell Culture
- DLP Bioprinters
- Extrustion Bioprinters
- Fluorescent Microscopy
- Microfluidic Bioprinters